
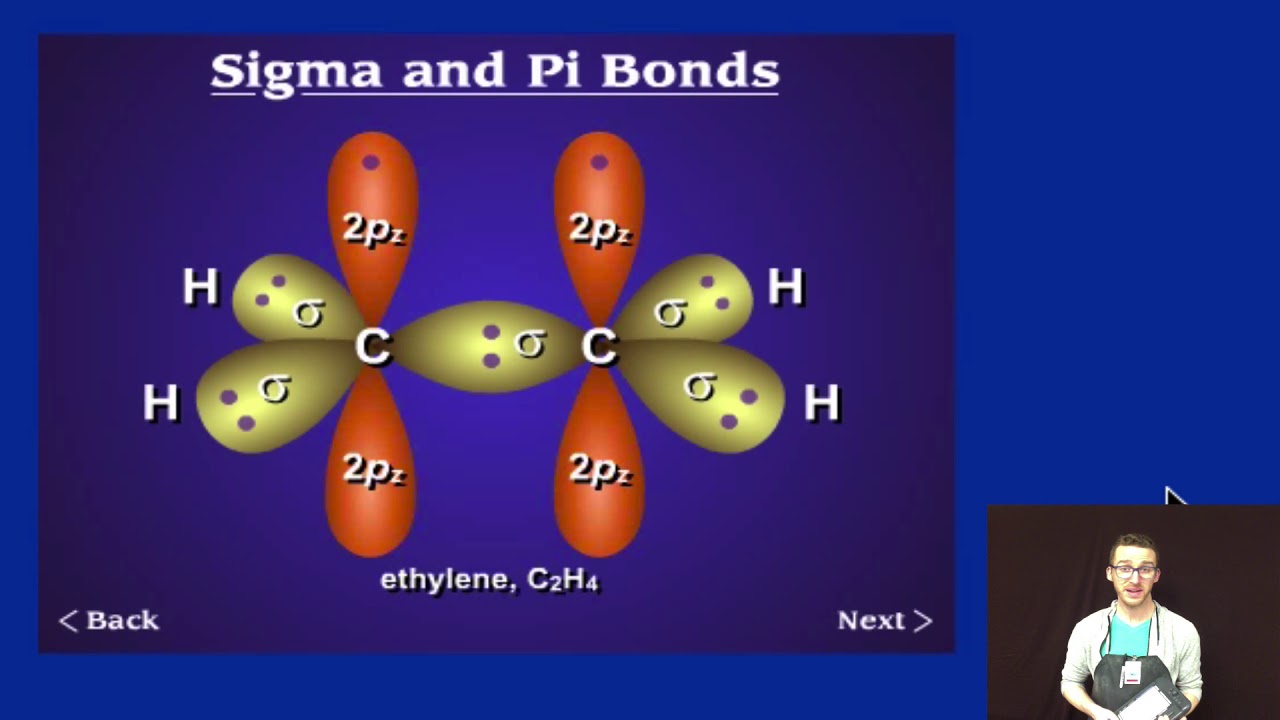
Overall, this was a sigma bond metathesis that exchanged a sigma bond with an alkyl group for a sigma bond with an #"H"#, and added a #pi# bond onto the dissociated alkyl group. The second step is a ligand dissociation of the alkene from the complex. (As a side note, 1,2-insertion is the second step shown here, which had followed a ligand association step.) That changed the hapticity of the alkyl group so that it now binds dihapto (via two atoms) as an alkene. The first step (including the transition state) is the reverse of 1,2-insertion, called #\mathbf(beta)# -hydride elimination. Thus, the process is neither oxidative nor reductive.ĮXAMPLE 2: TERMINATION OF CHAIN GROWTH IN OLEFIN POLYMERIZATION Bonding in more complicated molecules: Example: CH4. Note that the oxidation state of scandium did not change. A triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds (px+px and py+py). A sigma bond can be formed by overlap of an s atomic orbital with a p atomic orbital. It has cylindrical charge symmetry around the bond axis. This type of bond is referred to as a (sigma) bond. Atoms with pi bonds are less reactive than atoms having sigma bonds only. #R# can be any typical #R# group, like hydrogen, alkyl, etc. Atoms with sigma bonds are highly reactive. Next, we shall look at some examples of sigma and pi bonds in different molecules so that you are more familiar with the orbital interactions associated. #(eta^5-"C"_5"H"_5)_2"Sc""CH"_3# is the 15-electron complex called bis(pentahaptocyclopentadienyl)methylscandium(III), and demonstrates the ability of scandium to coordinate with all five carbons ( pentahapto) on cyclopentadiene. Which of the following compounds has the greatest amount of sigma bonds. It is important to note that this does not always happen in one step.Īn example is this process, involving #(eta^5-stackrel(color(red)(-1))("C"_5"H"_5))_2stackrel(color(blue)(+3))("Sc")stackrel(color(green)(-1))("CH"_3)# and, let's say, some alkane #"R"-"H"#:īy this paper, we can determine the transition state to look roughly like this: The pi bond is the 'second' bond of the double bonds between the carbon atoms, and is shown as an elongated green lobe that extends both above and below the plane of the molecule. Remember that covalent bonds form from the overlap of atomic orbitals which are just the space where electrons are likely to be found.Sigma bond metathesis is basically an "exchange" of a sigma bond that typically occurs with the transition metals on the first few columns (the "early" transition metals) that are in their highest oxidation state. Three sigma bonds are formed from each carbon atom for a total of six sigma bonds in the molecule. Saturated Unsaturated and Supersaturated.Reaction Quotient and Le Chatelier's Principle.In this case the unhybridized p orbital is of not much relevance. Multiple-bonded complexes edit Transition metal complexes that feature multiple bonds, such as the dihydrogen complex, have sigma bonds between the multiple bonded atoms. ( 83 votes) Flag Ganesh D 8 years ago Basically an orbital (be it s,p,d or f) is merely an area where there is a probability of finding an electron. Prediction of Element Properties Based on Periodic Trends For example, propane is described as consisting of ten sigma bonds, one each for the two CC bonds and one each for the eight CH bonds. The bonds between the sp 3 orbitals of hybridized carbon and the s orbitals of hydrogen in methane are also example of sigma bonds.Molecular Structures of Acids and Bases.

Sigma bonding can be an antibonding interaction or a bonding.

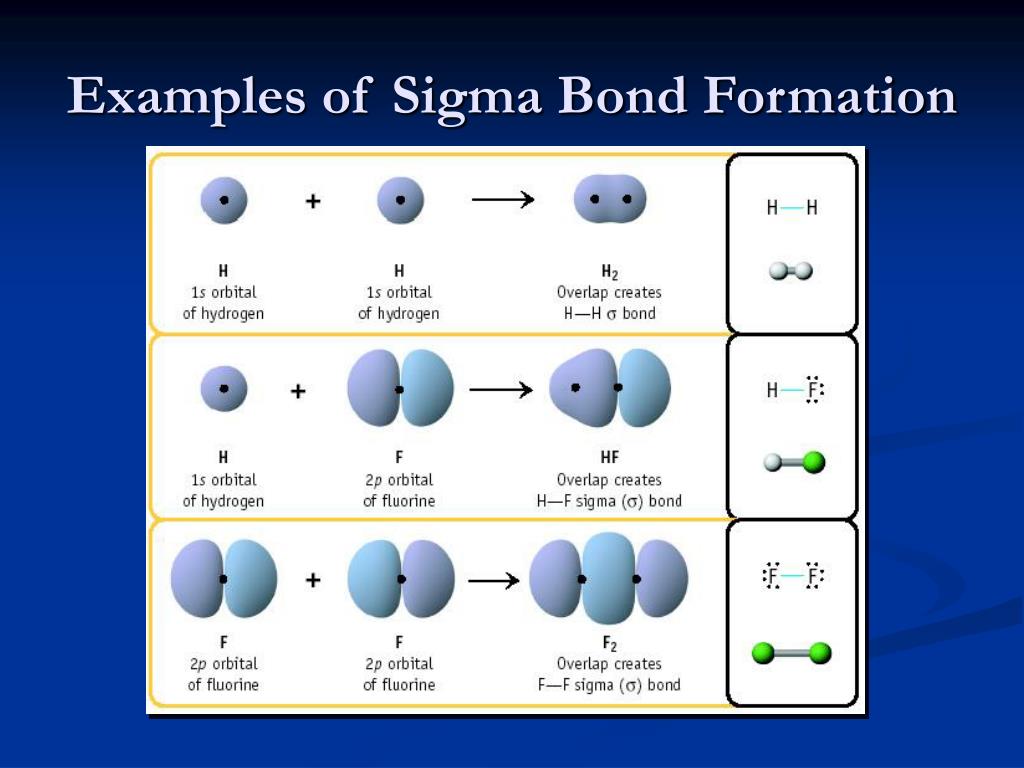
Ion and Atom Photoelectron Spectroscopy A sigma bond is a covalent bond which is formed by the head on overlap of two atomic orbitals.Elemental Composition of Pure Substances.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
